DATA_FILE1
Accessing objects by location and name:
Many HDF5 function calls use a combination of a location and name
to identify an HDF5 object.
The location will be specified by a location identifier, loc_id,
and will be an HDF5 file or an object in a file,
such as a group, dataset or named datatype.
The name, name, will be a character string and
will specify an object in an HDF5 file,
such as a group, dataset or named datatype.
name will specify that object by
either an absolute path in the file specified by loc_id
or by a relative path relative to loc_id.

|
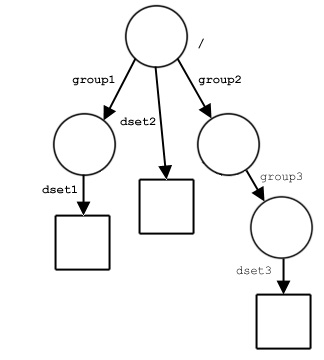
Sample file structure:DATA_FILE1
|
The loc_id and name combination,
as used in these function calls, can interact in any of several ways.
To illustrate, the following combinations all identify dset3
in the illustrated file structure.
loc_id is a file identifier,
name must specify the object from the file’s
root group, i.e., by an absolute path.
loc_id specifies the file DATA_FILE1.
name = '/group2/group3/dset3'
loc_id is a group identifier
and the object of interest is a member of that group,
name will simply be the name of the object.
loc_id specifies group3.
name = 'dset3'
loc_id is a group identifier
but the object of interest is not a direct member of that group,
name would generally specify the object by a relative
pathe, relative to that group.
loc_id specifies group2.
name = 'group3/dset3'
Alternatively, name could specify the object
with an absolute path in the file containing loc_id.
loc_id specifies group2.
name = '/group2/group3/dset3'
loc_id is the identifier of the object itself,
name should be a dot ( . ).
For those familiar with a UNIX shell, this works in much the
same manner as a dot ( . )
specifying the current working directory.
loc_id specifies dset3, the dataset itself.
name = '.'
Many HDF5 functions accept loc_id and name
in all of the above combinations.
When accepted combinations are limited for a specific function,
the limitations are mentioned in the function’s reference manual entry.
For a related discussion of the structure of HDF5 files and HDF5 path names, see “The Structure of an HDF5 File” (particularly the subsection “HDF5 Path Names and Navigation”) in the “HDF5 Data Model and File Structure” chapter of the HDF5 User’s Guide.