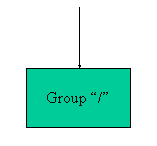Please see The HDF Group's new Support Portal for the latest information.
Contents:
Programming Example (C, Fortran, Java):
What is an HDF5 file?
An HDF5 file is a binary file containing scientific data and supporting metadata.
To create an HDF5 file, an application must specify not only a file name, but a file access mode, a file creation property list, and a file access property list. These terms are described below:
- File access mode:
When creating a file, the file access mode specifies the action to take if the file already exists:H5F_ACC_TRUNCspecifies that if the file already exists, the current contents will be deleted so that the application can rewrite the file with new data.H5F_ACC_EXCLspecifies that the open will fail if the file already exists. If the file does not already exist, the file access parameter is ignored.
In either case, the application has both read and write access to the successfully created file.
Note that there are two different access modes for opening existing files:
H5F_ACC_RDONLYspecifies that the application has read access but will not be allowed to write any data.H5F_ACC_RDWRspecifies that the application has read and write access.
- File creation property list:
The file creation property list is used to control the file metadata. File metadata contains information about the size of the user-block*, the size of various file data structures used by the HDF5 library, etc. In this tutorial, the default file creation property list,H5P_DEFAULT, is used.*The user-block is a fixed-length block of data located at the beginning of the file which is ignored by the HDF5 library. The user-block may be used to store any data or information found to be useful to applications.
- File access property list:
The file access property list is used to control different methods of performing I/O on files. It also can be used to control how a file is closed (whether or not to delay the actual file close until all objects in a file are closed). The default file access property list,H5P_DEFAULT, is used in this tutorial.
The steps to create and close an HDF5 file are as follows:
- 1. Specify the file creation and access property lists, if necessary.
- 2. Create the file.
- 3. Close the file, and if necessary, close the property lists.
Programming Example
Description
The following example code demonstrates how to create and close an HDF5 file.C:
#include "hdf5.h"
#define FILE "file.h5"
int main() {
hid_t file_id; /* file identifier */
herr_t status;
/* Create a new file using default properties. */
file_id = H5Fcreate(FILE, H5F_ACC_TRUNC, H5P_DEFAULT, H5P_DEFAULT);
/* Terminate access to the file. */
status = H5Fclose(file_id);
}
Fortran 90:
PROGRAM FILEEXAMPLE
USE HDF5 ! This module contains all necessary modules
IMPLICIT NONE
CHARACTER(LEN=8), PARAMETER :: filename = "filef.h5" ! File name
INTEGER(HID_T) :: file_id ! File identifier
INTEGER :: error ! Error flag
!
! Initialize FORTRAN interface.
!
CALL h5open_f (error)
!
! Create a new file using default properties.
!
CALL h5fcreate_f(filename, H5F_ACC_TRUNC_F, file_id, error)
!
! Terminate access to the file.
!
CALL h5fclose_f(file_id, error)
!
! Close FORTRAN interface.
!
CALL h5close_f(error)
END PROGRAM FILEEXAMPLE
See HDF5 Introductory Examples for the examples used in the Learning the Basics tutorial.
For details on compiling an HDF5 application: [ Compile Information ]
Remarks
In C: The include file
hdf5.hcontains definitions and declarations and must be included in any program that uses the HDF5 library.In FORTRAN: The module
HDF5contains definitions and declarations and must be used in any program that uses the HDF5 library. Also note that h5open_f MUST be called at the beginning of an HDF5 Fortran application (prior to any HDF5 calls) to initialize the library and variables. The h5close_f call MUST be at the end of the HDF5 Fortran application.- H5Fcreate / h5fcreate_f: Creates an HDF5 file and returns the file identifier.
For Fortran, the file creation property list and file access property list are optional. They can be omitted if the default values are to be used.
The root group is automatically created when a file is created. Every file has a root group and the path name of the root group is always
/. H5Fclose / h5fclose_f: Terminates access to an HDF5 file.
-
When an HDF5 file is no longer accessed by a program,
H5Fclose /
h5fclose_f
must be called to release the resources used by the file. This call
is mandatory.
Note that if H5Fclose / h5fclose_f is called for a file, but one or more objects within the file remain open, those objects will remain accessible until they are individually closed. This can cause access problems for other users, if objects were inadvertently left open. A File Access property controls how the file is closed.
File Contents
The HDF Group has developed tools for examining the contents of HDF5 files. The tool used throughout the HDF5 tutorial is the HDF5 dumper,h5dump,
which displays the file contents in human-readable form.
The output of h5dump is an ASCII display formatted according
to the HDF5 DDL grammar.
This grammar is defined, using Backus-Naur Form, in the
DDL in BNF for HDF5.
To view the HDF5 file contents, simply type:
h5dump <filename>Figure 4.1 describes the file contents of
file.h5 (filef.h5)
using a directed graph.
Fig. 4.1 Contents of file.h5 (filef.h5)
Figure 4.2 is the text description of
file.h5, as generated by
h5dump. The HDF5 file called file.h5 contains
a group called /, or the root group.
(The file called filef.h5,
created by the FORTRAN version of the example, has the same output except
that the filename shown is filef.h5.)
Fig. 4.2 file.h5 in DDL
HDF5 "file.h5" {
GROUP "/" {
}
}
File Definition in DDL
Figure 4.3 is the simplified DDL file definition for creating an HDF5 file. For simplicity, a simplified DDL is used in this tutorial. A complete and more rigorous DDL can be found in the DDL in BNF for HDF5, a section of the HDF5 User's Guide.Fig. 4.3 HDF5 File Definition
The following symbol definitions are used in the DDL:
::= defined as
<tname> a token with the name tname
<a> | <b> one of <a> or <b>
<a>* zero or more occurrences of <a>
The simplified DDL for file definition is as follows:
<file> ::= HDF5 "<file_name>" { <root_group> }
<root_group> ::= GROUP "/" { <group_attribute>*
<group_member>* }
<group_attribute> ::= <attribute>
<group_member> ::= <group> | <dataset>
- - Last modified: 21 December 2016