Please see The HDF Group's new Support Portal for the latest information.
In C it is done by selecting a hyperslab in a file that consists of regularly spaced columns. In F90, it is done by selecting a hyperslab in a file that consists of regularly spaced rows.
Figure a C Example
|
Figure b FORTRAN 90 Example |
|
|
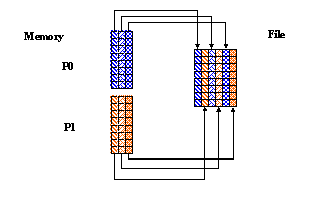
Writing Regularly Spaced Columns in C
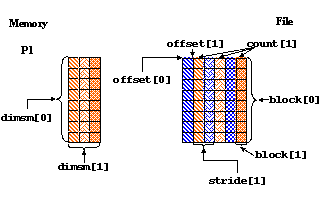
In this example, you have two processes that write to the same dataset, each writing to every other column in the dataset. For each process the hyperslab in the file is set up as follows:
89 count[0] = 1;
90 count[1] = dimsm[1];
91 offset[0] = 0;
92 offset[1] = mpi_rank;
93 stride[0] = 1;
94 stride[1] = 2;
95 block[0] = dimsf[0];
96 block[1] = 1;
The stride is 2 for dimension 1 to indicate that every other position
along this dimension will be written to. A stride of 1 indicates
that every position along a dimension will be written to.
For two processes, the mpi_rank will be either 0 or 1. Therefore:
- Process 0 writes to even columns (0, 2, 4...)
- Process 1 writes to odd columns (1, 3, 5...)
Below is an example program for writing hyperslabs by column in Parallel HDF5:
-
[ C Example ]
--
Hyperslab_by_col.c
HDF5 "SDS_col.h5" {
GROUP "/" {
DATASET "IntArray" {
DATATYPE H5T_STD_I32BE
DATASPACE SIMPLE { ( 8, 6 ) / ( 8, 6 ) }
DATA {
1, 2, 10, 20, 100, 200,
1, 2, 10, 20, 100, 200,
1, 2, 10, 20, 100, 200,
1, 2, 10, 20, 100, 200,
1, 2, 10, 20, 100, 200,
1, 2, 10, 20, 100, 200,
1, 2, 10, 20, 100, 200,
1, 2, 10, 20, 100, 200
}
}
}
}
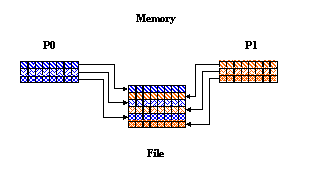
Writing Regularly Spaced Rows in FORTRAN 90
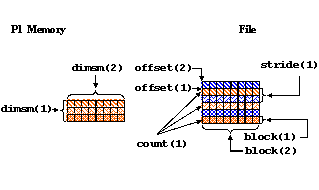
In this example, you have two processes that write to the same dataset, each writing to every other row in the dataset. For each process the hyperslab in the file is set up as follows:
83 ! Each process defines dataset in memory and writes it to
84 ! the hyperslab in the file.
85 !
86 count(1) = dimsm(1)
87 count(2) = 1
88 offset(1) = mpi_rank
89 offset(2) = 0
90 stride(1) = 2
91 stride(2) = 1
92 block(1) = 1
93 block(2) = dimsf(2)
The stride is 2 for dimension 1 to indicate that every other
position along this dimension will be written to. A stride
of 1 indicates that every position along a dimension will be written
to.
For two process, the mpi_rank will be either 0 or 1. Therefore:
- Process 0 writes to even rows (0, 2, 4 ...)
- Process 1 writes to odd rows (1, 3, 5 ...)
The following shows the data written by Process 1 to the file:
Below is the example program for writing hyperslabs by column in Parallel HDF5:
-
[ F90 Example ] --
hyperslab_by_row.f90
- - Last modified: 05 July 2016

