Please see The HDF Group's new Support Portal for the latest information.
Announcing HDF Server (h5serv) 0.2.0
We are proud to announce the availability of HDF Server (h5serv) 0.2.0!
HDF Server is a Python-based web service that can be used to send and receive HDF5 data using an HTTP-based REST interface. HDF Server supports CRUD (create, read, update, delete) operations on the full spectrum of HDF5 objects including: groups, links, datasets, attributes, and committed data types. As a REST service a variety of clients can be developed in JavaScript, Python, C, and other common languages.
The HDF Server extends the HDF5 data model to efficiently store large data objects (e.g. up to multi-TB data arrays) and access them over the web using a RESTful API. As datasets get larger and larger, it becomes impractical to download files to access data. Using HDF Server, data can be kept in one central location and content vended via well-defined URIs. This enables exploration and analysis of the data while minimizing the number of bytes that need to be transmitted over the network.
Since HDF Server supports both reading and writing of data, it enables some interesting scenarios such as:
- Collaborative annotation of data sets
- Compute clusters that use HDF Server for data access
- Continually updated data shares (e.g. Stock Market quotes, sensor data)
- Storing the analysis of the data (say a visualization) with the original source data
In addition to these, we would like to hear your ideas of how HDF Server could be utilized (as well as any other feedback you might have). Additional information follows below.
Thanks to everyone who helped and advised on this project.
Contents:
- HDF REST
- HDF5 JSON
- AWS Instance
- Install Locally
- What's new in HDF Server (h5serv) 0.2.0
- Previous release HDF Server 0.1.0
- Features not included in this release (but planned for future releases)
- Feedback
- Links
HDF REST
The HDF REST API enables access to HDF5 data objects via a combination of standard HTTP verbs:
GET, PUT, POST, DELETE acting on HDF5 objects identified via URIs (Uniform Resource Identifier).
For example, POST /groups creates a new group. Collections of HDF objects
(that would normally be stored in a file) are mapped as Internet domains.
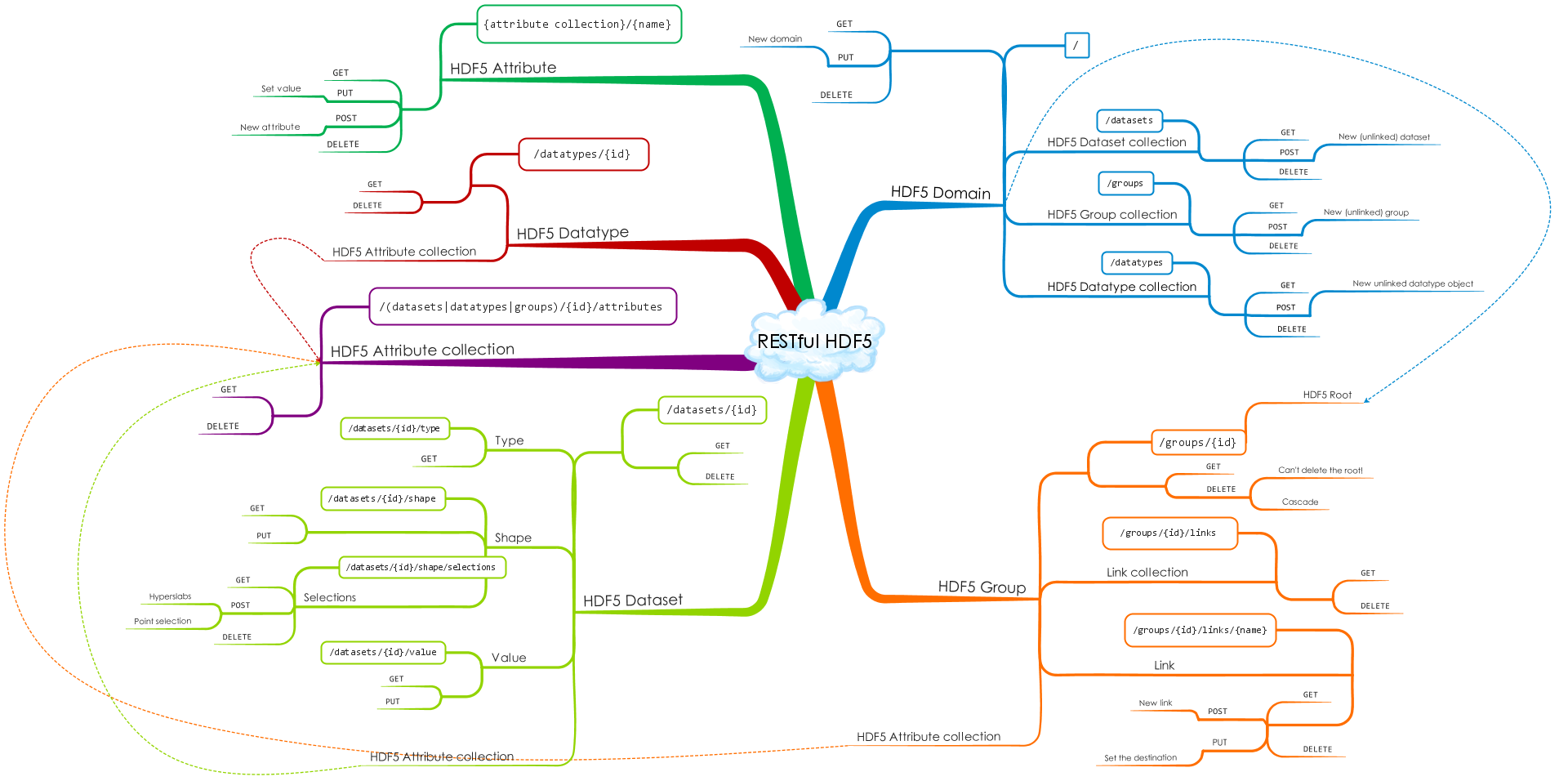
To see how this works, you can try this out using an instance of the server we set up on AWS. Go to this link: https://data.hdfgroup.org:7258/?host=tall.data.hdfgroup.org and you should see text that provides basic information about the data collection "tall" (originally from the file tall.h5 that is included in the HDF5 library release). The text displayed is the JSON representation of the domain (if you install a JSON plugin for your browser that will "prettify" the rendering). As you can see from the somewhat cryptic response text, the server is designed to be used as a Web API rather than a Web UI (though it is certainly possible to write a Web UI using the server as the data source).
Similarly, each group, dataset, and attribute is accessible as a URI within that domain. For example, to read an attribute you would use a URL like this: https://data.hdfgroup.org:7258/groups/4af80138-3e8a-11e6-a48f-0242ac110003/attributes/attr2?host=tall.data.hdfgroup.org. When reading the dataset values, you may desire to only request a sub-region of the dataset. To do so, use a select query that specifies that start, stop, and step values that defines the region to be returned. E.g.: this request: https://data.hdfgroup.org:7258/datasets/4af8bc72-3e8a-11e6-a48f-0242ac110003/value?host=tall.data.hdfgroup.org&select=[0:4,0:4] returns a 4x4 subset of a 10x10 array.
As you may have noticed from the URLs above, objects are identified via a UUID (universally unique identifier) rather than (potentially ambiguous) path names. This has the advantage that each group and dataset object has a unique representation. HDF5 links can then reference the UUID of the linked object. Furthermore, this uniformity of the URL structure decouples server and client, since no a priori knowledge of the HDF5 path name space is necessary.
Besides reading data, HDF Server supports the full set of create, update, and delete operations (comparable to what you would find in the HDF5 library) using respectively the http POST, PUT, and DELETE operations. Though PUT, POST, and DELETE operations can't be invoked directly from the browser address bar, the release includes a large set of test programs that provides examples of how to use all the operations supported by the server.
HDF5 JSON
HDF Server uses JSON as the default representation for requests and responses, so one aspect of this project was defining JSON representations of HDF5 objects. We were able to utilize this code to create utilities which can convert from HDF5 to JSON formats and vice-versa (these are included with the project). An HDF5 JSON grammar can be found here: http://hdf5-json.readthedocs.org/.
AWS Instance
The HDF Group is running an instance of the service on Amazon AWS reachable via the endpoint: data.hdgroup.org:7253 for non-SSL or data.hdgroup.org:7258 for SSL. This endpoint can be used to read and write data using the REST API (for experimentation purposes only!).
Web UI
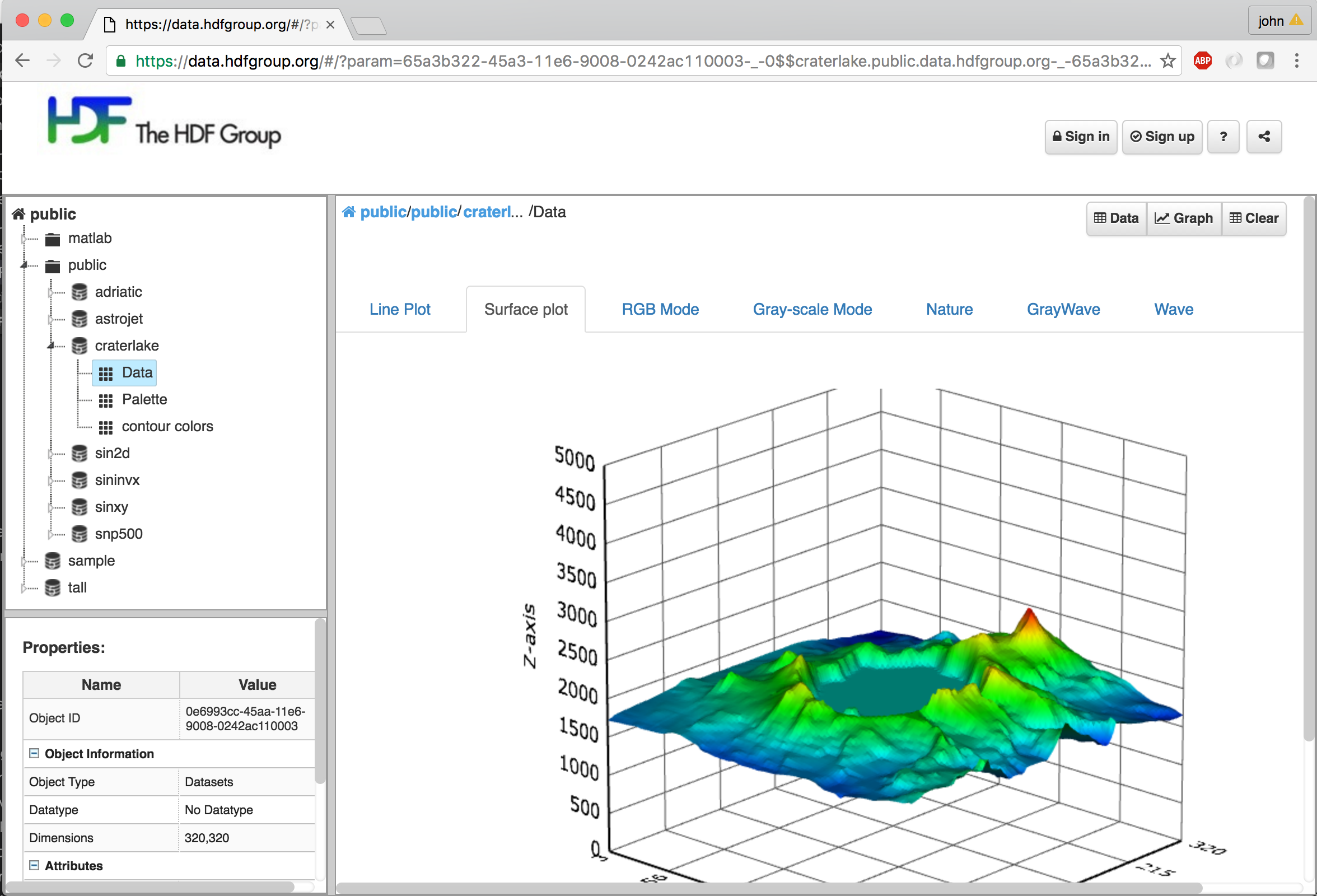
An experimental AJAX_based web UI is available at: https://data.hdfgroup.org. The Web UI provides an HDFView like interface in a browser for viewing data that is hosted by the HDF Server. In addition to a grid view, simple line, image, and 3D plots can be displayed. For example:
Install Locally
As a self-contained web service, HDF Server is quite easy to install and run on your own system (no Apache server required!). Complete instructions can be found here:
http://h5serv.readthedocs.org/en/latest/Installation/ServerSetup.html
What's new in HDF Server (h5serv) 0.2.0
-
Authentication is supported via HTTP Basic authentication. Other authentication methods can be supported via plugins. See the blog post: https://www.hdfgroup.org/2015/12/serve-protect-web-security-hdf5/ for a review of authentication with HDF Server. This covers ACLs (see below) as well.
-
Access Control - Permissions for Read and write access to entire files or individual HDF objects (groups, datasets, named data types) can be controlled using Access Control Lists (ACL). ACL's can be associated with any object to define which users can perform which action. ACLs can be setup either through the REST API itself or using admin tools included with the release.
-
Table of Contents - All the files hosted by the Server are not discoverable via the "Table of Contents" (TOC). The TOC is a special HDF5 file that contains external links to other files hosted by the server. You can see the root group of the TOC here: https://data.hdfgroup.org:7258/groups/65a37100-45a3-11e6-9008-0242ac110003/links. The TOC is automatically updated as new files (domains) are added or deleted.
-
Binary Data Transfer - Request to read or write dataset values can be done using JSON or binary data. If the client supports it binary transfers are much faster for large requests.
-
Variable length datatypes - Variable length datatypes are now supported.
-
Python client SDK - Python developers can use the h5pyd package: https://github.com/HDFGroup/h5pyd to access HDF Server content without directly using the REST API. h5pyd is compatible with the high-level routines in the commonly used h5py package (see for a guide of methods supported in h5py and h5pyd).
Previous Release - HDF Server (h5serv) 0.1.0
This was the first release of HDF Server. Major aspects of this release are:
-
Implementation of the REST API as outlined in the RESTful HDF5 paper:
https://support.hdfgroup.org/pubs/papers/RESTful_HDF5.pdf -
A simple DNS Server that maps DNS domains to HDF5 collections (i.e. files)
-
Utilities to convert native HDF5 files to HDF5-JSON and HDF5-JSON to HDF5
-
UUID and timestamp extensions for HDF5 datasets, groups, and committed data types
Note: This release of h5serv should be viewed as a reference release of the HDF5 REST API, and not suitable for production use on the public Internet.
Features not included in this release (but planned for future releases)
-
HDF5 compatible library ‐ C/C++ applications can invoke http requests using libraries such as libcurl, but an HDF5 library compatible client is not part of the current release.
-
High Performance usage ‐ the current release of h5serv serializes all requests, so would not be suitable for a demanding environment with a large number of clients and/or high throughput rates.
-
Some HDF5 data types are not yet supported. Namely: Bitfields and Opaque types.
Feedback
We would like to hear your thoughts on HDF Server, including:
- Issues with the code or documentation
- Ideas or questions on how it could be utilized
- Suggestions for features or enhancements
- Questions on how well HDF Server would work for different data sets or use cases
Please submit feedback using one of the links below.
Watch https://www.hdfgroup.org/blog for previous and upcoming posts about HDF Server.
Links
Download: https://github.com/HDFGroup/h5serv
Documentation: http://h5serv.readthedocs.org/en/latest/index.html
Report bugs at: https://github.com/HDFGroup/h5serv/issues
Submit fixes/enhancements at: https://github.com/HDFGroup/h5serv/pulls
General comments or feedback should be sent to the HDF-Forum. See the Community Support page for more details on joining and viewing HDF-Forum messages.
- - Last modified: 12 October 2016