DATA_FILE1
The C Interfaces:
| * Use of these functions is deprecated in Release 1.8.0. | ||||
| * Use of these functions is deprecated in Release 1.8.0. | ||||
The Attribute interface, H5A, is primarily designed to easily allow small datasets to be attached to primary datasets as metadata information. Additional goals for the H5A interface include keeping storage requirement for each attribute to a minimum and easily sharing attributes among datasets.
Because attributes are intended to be small objects, large datasets intended as additional information for a primary dataset should be stored as supplemental datasets in a group with the primary dataset. Attributes can then be attached to the group containing everything to indicate a particular type of dataset with supplemental datasets is located in the group. How small is "small" is not defined by the library and is up to the user’s interpretation.
See “HDF5 Attributes” in the HDF5 User’s Guide for more information.
Location and name with attribute functions:

|
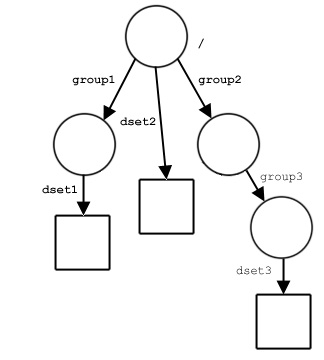
Sample file structure:DATA_FILE1
|
H5Acreate2,
use a location identifier, an object name, and an attribute name,
loc_id, obj_name, and attr_name,
respectively.
loc_id and obj_name specify the object to which
an attribute is attached and carry exactly the same meaning and
interaction modes as described for loc_id and name
in “Accessing objects by location
and name.”
attr_name specifies the attribute as it is attached to
that object.
The following example specifies an attribute named A3
attached to the dataset dset3.
loc_id specifies group3.
name = 'dset3'
attr_name = 'A3'
H5Acreate1,
generally use only a location identifier and a name.
In these functions, loc_id fully specifies
the object to which an attribute is attached; the attribute itself
is specified by an attribute name, attr_name.
Again, the following example specifies an attribute named A3
attached to the dataset dset3 above.
loc_id specifies dset3.
attr_name = 'A3'
H5Aclose(hid_t attr_id)
H5Aclose terminates access to the attribute
specified by attr_id by releasing the identifier.
Further use of a released attribute identifier is illegal; a function using such an identifier will fail.
hid_t attr_id |
IN: Attribute to release access to. |
SUBROUTINE h5aclose_f(attr_id, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(OUT) :: attr_id ! Attribute identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE h5aclose_f
H5Acreate is a macro that is mapped to either
H5Acreate1 or
H5Acreate2,
depending on the needs of the application.
Such macros are provided to facilitate application compatibility. For example:
H5Acreate macro
will be mapped to H5Acreate1 and
will use the H5Acreate1 syntax
(first signature above)
if an application is coded for HDF5 Release 1.6.x.
H5Acreate macro
mapped to H5Acreate2 and
will use the H5Acreate2 syntax
(second signature above)
if an application is coded for HDF5 Release 1.8.x.
Macro use and mappings are fully described in “API Compatibility Macros in HDF5”; we urge you to read that document closely.
When both the HDF5 Library and the application are built and
installed with no specific compatibility flags,
H5Acreate is mapped to the most recent version of
the function, currently
H5Acreate2.
If the library and/or application is compiled for Release 1.6
emulation, H5Acreate will be mapped to
H5Acreate1.
Function-specific flags are available to override these settings
on a function-by-function basis when the application is compiled.
Specific compile-time compatibility flags and the resulting mappings are as follows:
| Compatibility setting | H5Acreate mapping |
|---|---|
Global settings |
|
| No compatibility flag | H5Acreate2 |
| Enable deprecated symbols | H5Acreate2 |
| Disable deprecated symbols | H5Acreate2 |
Emulate Release 1.6 interface |
H5Acreate1 |
Function-level macros |
|
H5Acreate_vers = 2 |
H5Acreate2 |
H5Acreate_vers = 1 |
H5Acreate1 |
The attribute identifier returned by this macro must be released
with H5Aclose or resource leaks will develop.
H5Acreate interface
and the only interface available prior to HDF5 Release 1.8.0.
This signature and the corresponding function are now deprecated
but will remain directly callable as
H5Acreate1.
Signature [2] above was introduced with HDF5 Release 1.8.0
and is the recommended and default interface.
It is directly callable as
H5Acreate2.
See “API Compatibility Macros in HDF5” for circumstances under which either of these functions might not be available in an installed instance of the HDF5 Library.
SUBROUTINE h5acreate_f(loc_id, name, type_id, space_id, attr_id, hdferr, &
acpl_id, aapl_id )
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: loc_id ! Object identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: name ! Attribute name
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: type_id ! Attribute datatype identifier
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: space_id ! Attribute dataspace identifier
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(OUT) :: attr_id ! Attribute identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: acpl_id
! Attribute creation property
! list identifier
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: aapl_id
! Attribute access property
! list identifier
END SUBROUTINE h5acreate_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 |
The function H5Acreate renamed to
H5Acreate1 and deprecated in this release.
The macro H5Acreate
and the functions H5Acreate2 and
H5Acreate_by_name
introduced in this release. |
H5Acreate1(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *attr_name,
hid_t type_id,
hid_t space_id,
hid_t acpl_id
)
H5Acreate2.
H5Acreate1 creates the attribute attr_name
attached to the object specified with loc_id.
The attribute name specified in attr_name must be unique.
Attempting to create an attribute with the same name as an already
existing attribute will fail, leaving the pre-existing attribute
in place. To overwrite an existing attribute with a new attribute
of the same name, first call H5Adelete then recreate
the attribute with H5Acreate1.
The datatype and dataspace identifiers of the attribute,
type_id and space_id, respectively,
are created with the H5T and H5S interfaces, respectively.
Currently only simple dataspaces are allowed for attribute dataspaces.
The attribute creation property list, acpl_id,
is currently unused;
it may be used in the future for optional attribute properties.
At this time, H5P_DEFAULT is the only accepted value.
H5Aclose or resource leaks will develop.
hid_t loc_id |
IN: Identifier for the object to which the
attribute is to be attached
May be any HDF5 object identifier (group, dataset, or committed datatype) or an HDF5 file identifier; if loc_id is a file identifer, the attribute
will be attached to that file’s root group. |
const char *attr_name |
IN: Name of attribute to create |
hid_t type_id |
IN: Identifier of datatype for attribute |
hid_t space_id |
IN: Identifier of dataspace for attribute |
hid_t acpl_id |
IN: Identifier of creation property list
(Currently not used; specify H5P_DEFAULT.) |
H5Acreate.
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 |
The function H5Acreate renamed to
H5Acreate1 and deprecated in this release. |
H5Acreate2(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *attr_name,
hid_t type_id,
hid_t space_id,
hid_t acpl_id,
hid_t aapl_id,
)
H5Acreate2 creates an attribute, attr_name,
which is attached to the object specified by the identifier
loc_id.
The attribute name, attr_name, must be unique for
the object.
The attribute is created with the specified datatype and dataspace,
type_id and space_id,
which are created with the H5T and H5S interfaces, respectively.
If type_id is either a fixed-length or
variable-length string, it is important to set the string length
when defining the datatype.
String datatypes are derived from H5T_C_S1
(or H5T_FORTRAN_S1 for Fortran codes),
which defaults to 1 character in size.
See H5Tset_size and
“Creating
variable-length string datatypes.”
The access property list is currently unused, but will be used in the future.
This property list should currently be H5P_DEFAULT.
The attribute identifier returned by this function must be released
with H5Aclose
or resource leaks will develop.
hid_t loc_id
|
IN: Location or object identifier
May be any HDF5 object identifier (group, dataset, or committed datatype) or an HDF5 file identifier; if loc_id is a file identifer, the attribute
will be attached to that file’s root group.
|
const char *attr_name
|
IN: Attribute name |
hid_t type_id
|
IN: Attribute datatype identifier |
hid_t space_id
|
IN: Attribute dataspace identifier |
hid_t acpl_id
|
IN: Attribute creation property list identifier
(Currently not used; specify H5P_DEFAULT.)
|
hid_t aapl_id
|
IN: Attribute access property list identifier
(Currently not used; specify H5P_DEFAULT.)
|
H5Acreate.
H5Tset_size
| Release | Change |
| 1.8.0 | C function introduced in this release. |
H5Acreate_by_name(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *obj_name,
const char *attr_name,
hid_t type_id,
hid_t space_id,
hid_t acpl_id,
hid_t aapl_id,
hid_t lapl_id
)
H5Acreate_by_name creates an attribute,
attr_name, which is attached to the object specified
by loc_id and obj_name.
loc_id is a location identifier;
obj_name is the object name relative to loc_id.
If loc_id fully specifies the object to which the
attribute is to be attached, obj_name should be
'.' (a dot).
The attribute name, attr_name, must be unique for
the object.
The attribute is created with the specified datatype and dataspace,
type_id and space_id,
which are created with the H5T and H5S interfaces respectively.
The attribute creation and access property lists are currently unused,
but will be used in the future for optional attribute creation
and access properties.
These property lists should currently be H5P_DEFAULT.
The link access property list, lapl_id,
may provide information regarding the properties of links
required to access the object, obj_name.
See “Link Access Properties” in the
H5P APIs.
The attribute identifier returned by this function must be released
with H5Aclose
or resource leaks will develop.
hid_t loc_id
|
IN: Location or object identifier; may be dataset or group |
const char *obj_name
|
IN: Name, relative to loc_id,
of object that attribute is to be attached to
|
const char *attr_name
|
IN: Attribute name |
hid_t type_id
|
IN: Attribute datatype identifier |
hid_t space_id
|
IN: Attribute dataspace identifier |
hid_t acpl_id
|
IN: Attribute creation property list identifier
(Currently not used.) |
hid_t aapl_id
|
IN: Attribute access property list identifier
(Currently not used.) |
hid_t lapl_id
|
IN: Link access property list |
SUBROUTINE h5acreate_by_name_f(loc_id, obj_name, attr_name, type_id, space_id, &
attr, hdferr, acpl_id, aapl_id, lapl_id)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: loc_id ! Object identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: obj_name ! Name of object to which
! attribute is attached
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: attr_name ! Attribute name
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: type_id ! Attribute datatype identifier
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: space_id ! Attribute dataspace identifier
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(OUT) :: attr ! An attribute identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: acpl_id
! Attribute creation property list
! identifier (Currently not used.)
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: aapl_id
! Attribute access property list
! identifier (Currently not used.)
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: lapl_id
! Link access property list
END SUBROUTINE h5acreate_by_name_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Adelete(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *attr_name
)
H5Adelete removes the attribute specified by its
name, attr_name, from a dataset, group, or named datatype.
This function should not be used when attribute identifiers are
open on loc_id as it may cause the internal indexes
of the attributes to change and future writes to the open
attributes to produce incorrect results.
hid_t loc_id |
IN: Identifier of the dataset, group, or named datatype to have the attribute deleted from. |
const char *attr_name |
IN: Name of the attribute to delete. |
SUBROUTINE h5adelete_f(obj_id, name, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: obj_id ! Object identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: name ! Attribute name
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE h5adelete_f
| Release | C |
H5Adelete_by_name(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *obj_name,
const char *attr_name,
hid_t lapl_id
)
H5Adelete_by_name removes the attribute
attr_name from an object specified by location and name,
loc_id and obj_name, respectively.
If loc_id fully specifies the object from which the
attribute is to be removed, obj_name should be
'.' (a dot).
The link access property list, lapl_id,
may provide information regarding the properties of links
required to access the object, obj_name.
See “Link Access Properties” in the
H5P APIs.
hid_t loc_id
| IN: Location or object identifier; may be dataset or group |
const char *obj_name
|
IN: Name of object, relative to location, from which attribute is to be removed |
const char *attr_name
|
IN: Name of attribute to delete |
hid_t lapl_id
|
IN: Link access property list |
SUBROUTINE h5adelete_by_name_f(loc_id, obj_name, attr_name, hdferr, lapl_id)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: loc_id ! Identifer for object to which
! attribute is attached
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: obj_name
! Name of object, relative to location,
! from which attribute is to be removed
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: attr_name
! Name of attribute to delete
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: lapl_id
! Link access property list
END SUBROUTINE h5adelete_by_name_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Adelete_by_idx(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *obj_name,
H5_index_t idx_type,
H5_iter_order_t order,
hsize_t n,
hid_t lapl_id
)
H5Adelete_by_idx removes an attribute, specified by its
location in an index, from an object.
The object from which the attribute is to be removed
is specified by a location identifier and name,
loc_id and obj_name, respectively.
If loc_id fully specifies the object from which the
attribute is to be removed, obj_name should be
'.' (a dot).
The attribute to be removed is specified by
a position in an index, n.
The type of index is specified by idx_type and may be
H5_INDEX_NAME, for an alpha-numeric index by name, or
H5_INDEX_CRT_ORDER, for an index by creation order.
The order in which the index is to be traversed is specified by
order and may be
H5_ITER_INC (increment) for top-down iteration,
H5_ITER_DEC (decrement) for bottom-up iteration, or
H5_ITER_NATIVE, in which case HDF5 will iterate in the
fastest-available order.
For example, if idx_type, order, and
n are set to H5_INDEX_NAME,
H5_ITER_INC, and 5, respectively,
the fifth attribute by alpha-numeric order of attribute names
will be removed.
For a discussion of idx_type and order,
the valid values of those parameters, and
the use of n,
see the description of H5Aiterate2
The link access property list, lapl_id,
may provide information regarding the properties of links
required to access the object, obj_name.
See “Link Access Properties” in the
H5P APIs.
hid_t loc_id
|
IN: Location or object identifier; may be dataset or group |
const char *obj_name
|
IN: Name of object, relative to location, from which attribute is to be removed |
H5_index_t idx_type
|
IN: Type of index |
H5_iter_order_t order
|
IN: Order in which to iterate over index |
hsize_t n
|
IN: Offset within index |
hid_t lapl_id
|
IN: Link access property list |
SUBROUTINE h5adelete_by_idx_f(loc_id, obj_name, idx_type, order, n, hdferr, &
lapl_id)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T),INTENT(IN) :: loc_id
! Identifer for object to which
! attribute is attached
CHARACTER(LEN=*),INTENT(IN) :: obj_name
! Name of object, relative to location,
! from which attribute is to be removed
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: idx_type
! Type of index; Possible values are:
! H5_INDEX_UNKNOWN_F - Unknown index type
! H5_INDEX_NAME_F - Index on names
! H5_INDEX_CRT_ORDER_F - Index on creation order
! H5_INDEX_N_F - Number of indices defined
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: order
! Order in which to iterate over index:
! H5_ITER_UNKNOWN_F - Unknown order
! H5_ITER_INC_F - Increasing order
! H5_ITER_DEC_F - Decreasing order
! H5_ITER_NATIVE_F - No particular order,
! whatever is fastest
! H5_ITER_N_F - Number of iteration orders
INTEGER(HSIZE_T), INTENT(IN) :: n
! Offset within index
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr
! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: lapl_id
! Link access property list
END SUBROUTINE h5adelete_by_idx_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aexists(
hid_t obj_id,
const char *attr_name
)
H5Aexists determines
whether the attribute attr_name exists
on the object specified by obj_id.
hid_t obj_id,
|
IN: Object identifier |
const char *attr_name
|
IN: Attribute name |
attr_name exists.
attr_name does not exist.
SUBROUTINE h5aexists_f(obj_id, attr_name, attr_exists, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: obj_id ! Object identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: attr_name ! Attribute name
LOGICAL, INTENT(OUT) :: attr_exists ! .TRUE. if exists, .FALSE. otherwise
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aexists_by_name(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *obj_name,
const char *attr_name,
hid_t lapl_id
)
H5Aexists_by_name determines
whether the attribute attr_name exists on an object.
That object is specified by its location and name,
loc_id and obj_name, respectively.
loc_id specifies a location in the file containing
the object.
obj_name is the name of the object
to which the attribute is attached and can be
a relative name, relative to loc_id, or
an absolute name, based in the root group of the file.
If loc_id fully specifies the object,
obj_name should be '.' (a dot).
The link access property list, lapl_id,
may provide information regarding the properties of links
required to access obj_name.
See “Link Access Properties” in the
H5P APIs.
hid_t loc_id,
|
IN: Location identifier |
const char *obj_name
|
IN: Object name Either relative to loc_id,
absolute from the file’s root group,
or '.' (a dot)
|
const char *attr_name
|
IN: Attribute name |
hid_t lapl_id
|
IN: Link access property list identifier |
attr_name exists.
attr_name does not exist.
SUBROUTINE h5aexists_by_name_f(loc_id, obj_name, attr_name, attr_exists, hdferr,&
lapl_id)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: loc_id ! Location identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: obj_name
! Object name either relative to loc_id,
! absolute from the
! file’s root group, or '.'
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: attr_name
! Attribute name
LOGICAL, INTENT(OUT) :: attr_exists ! .TRUE. if exists, .FALSE. otherwise
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: lapl_id
! Link access property list identifier
END SUBROUTINE h5aexists_by_name_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aget_create_plist(hid_t attr_id)
H5Aget_create_plist returns an identifier
for the attribute creation property list associated with the
attribute specified by attr_id.
The creation property list identifier should be released with
H5Pclose.
hid_t attr_id |
IN: Identifier of the attribute. |
SUBROUTINE h5aget_create_plist_f(attr_id, creation_prop_id, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: attr_id
! Identifier of the attribute
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(OUT) :: creation_prop_id
! Identifier for the attribute’s creation property
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr
! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE h5aget_create_plist_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aget_info(
hid_t attr_id,
H5A_info_t *ainfo
)
H5Aget_info retrieves attribute information,
locating the attribute with an attribute identifier,
attr_id, which is the identifier returned by
H5Aopen or
H5Aopen_by_idx.
The attribute information is returned in the ainfo struct.
The ainfo struct is defined as follows:
typedef struct {
hbool_t corder_valid;
H5O_msg_crt_idx_t corder;
H5T_cset_t cset;
hsize_t data_size;
} H5A_info_t;
corder_valid indicates whether the creation order data
is valid for this attribute. Note that if creation order is not being tracked,
no creation order data will be valid. Valid values are TRUE
and FALSE.
corder is a positive integer containing the creation order
of the attribute. This value is 0-based, so, for example,
the third attribute created will have a corder value of
2.
cset indicates the character set used for the attribute’s
name; valid values are defined in H5Tpublic.h and
include the following:
H5T_CSET_ASCII
| US ASCII | |
H5T_CSET_UTF8
| UTF-8 Unicode encoding |
H5Pset_char_encoding.
data_size indicates the size, in the number of characters,
of the attribute.
hid_t attr_id
|
IN: Attribute identifier |
H5A_info_t *ainfo
|
OUT: Attribute information struct |
SUBROUTINE h5aget_info_f(attr_id, f_corder_valid, corder, cset, data_size,hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: attr_id ! Attribute identifier
LOGICAL, INTENT(OUT) :: f_corder_valid ! Indicates whether the creation order
! data is valid for this attribute
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: corder ! Is a positive integer containing the
! creation order of the attribute
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: cset ! Indicates the character set used for
! the ! attribute’s name
INTEGER(HSIZE_T), INTENT(OUT) :: data_size
! Indicates the size, in the number
! of characters, of the attribute
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE h5aget_info_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aget_info_by_idx(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *obj_name,
H5_index_t idx_type,
H5_iter_order_t order,
hsize_t n,
H5A_info_t *ainfo,
hid_t lapl_id
)
H5Aget_info_by_idx retrieves information for an
attribute that is attached to an object, which is specified by
its location and name, loc_id and obj_name,
respectively.
The attribute is located by its index position and the
attribute information is returned in the ainfo struct.
If loc_id fully specifies the object to which the
attribute is attached, obj_name should be
'.' (a dot).
The attribute is located by means of an index type,
an index traversal order, and a position in the index,
idx_type, order and n,
respectively.
These parameters and their valid values are discussed in the
description of H5Aiterate2.
The ainfo struct, which will contain the returned
attribute information, is described in
H5Aget_info.
The link access property list, lapl_id,
may provide information regarding the properties of links
required to access the object, obj_name.
See “Link Access Properties” in the
H5P APIs.
hid_t loc_id
|
IN: Location of object to which attribute is attached |
const char *obj_name
|
IN: Name of object to which attribute is attached, relative to location |
H5_index_t idx_type
|
IN: Type of index |
H5_iter_order_t order
|
IN: Index traversal order |
hsize_t n
|
IN: Attribute’s position in index |
H5A_info_t *ainfo
|
OUT: Struct containing returned attribute information |
hid_t lapl_id
|
IN: Link access property list |
SUBROUTINE h5aget_info_by_idx_f(loc_id, obj_name, idx_type, order, n, &
f_corder_valid, corder, cset, data_size, hdferr, lapl_id)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: loc_id
! Object identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: obj_name
! Name of object to which attribute is attached
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: idx_type
! Type of index; Possible values are:
! H5_INDEX_UNKNOWN_F - Unknown index type
! H5_INDEX_NAME_F - Index on names
! H5_INDEX_CRT_ORDER_F - Index on creation order
! H5_INDEX_N_F - Number of indices defined
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: order
! Order in which to iterate over index:
! H5_ITER_UNKNOWN_F - Unknown order
! H5_ITER_INC_F - Increasing order
! H5_ITER_DEC_F - Decreasing order
! H5_ITER_NATIVE_F - No particular order,
! whatever is fastest
INTEGER(HSIZE_T), INTENT(IN) :: n
! Attribute’s position in index
LOGICAL, INTENT(OUT) :: f_corder_valid
! Indicates whether the creation order data is
! valid for this attribute
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: corder
! Is a positive integer containing the creation
!order of the attribute
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: cset
! Indicates the character set used for the
! attribute’s name
INTEGER(HSIZE_T), INTENT(OUT) :: data_size
! Indicates the size, in the number of characters,
! of the attribute
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr
! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: lapl_id
! Link access property list
END SUBROUTINE h5aget_info_by_idx_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aget_info_by_name(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *obj_name,
const char *attr_name,
H5A_info_t *ainfo,
hid_t lapl_id
)
H5Aget_info_by_name retrieves
information for an attribute, attr_name,
that is attached to an object, specified by its location and name,
loc_id and obj_name, respectively.
The attribute information is returned in the ainfo struct.
If loc_id fully specifies the object to which the
attribute is attached, obj_name should be
'.' (a dot).
The ainfo struct is described in
H5Aget_info.
The link access property list, lapl_id,
may provide information regarding the properties of links
required to access the object, obj_name.
See “Link Access Properties” in the
H5P APIs.
hid_t loc_id
|
IN: Location of object to which attribute is attached |
const char *obj_name
|
IN: Name of object to which attribute is attached, relative to location |
const char *attr_name
|
IN: Attribute name |
H5A_info_t *ainfo
|
OUT: Struct containing returned attribute information |
hid_t lapl_id
|
IN: Link access property list |
SUBROUTINE h5aget_info_by_name_f(loc_id, obj_name, attr_name, &
f_corder_valid, corder, cset, data_size, hdferr, lapl_id)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: loc_id ! Object identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: obj_name ! Name of object to which attribute
! is attached
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: attr_name ! Attribute name
LOGICAL, INTENT(OUT) :: f_corder_valid ! Indicates whether the creation
! order data is valid for this
! attribute
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: corder ! Is a positive integer containing
! the creation order of the
! attribute
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: cset ! Indicates the character set used
! for the attribute’s name
INTEGER(HSIZE_T), INTENT(OUT) :: data_size ! Indicates the size, in the number
! of characters, of the attribute
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: lapl_id
! Link access property list
END SUBROUTINE h5aget_info_by_name_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aget_name(hid_t attr_id,
size_t buf_size,
char *buf
)
H5Aget_name retrieves the name of an attribute
specified by the identifier, attr_id. Up to
buf_size characters are stored in buf followed by
a \0 string terminator. If the name of the attribute is longer
than (buf_size -1), the string terminator is stored
in the last position of the buffer to properly terminate the string.
If the user only wants to find out the size of this name,
the values 0 and NULL
can be passed in for the parameters bufsize and
buf.
hid_t attr_id |
IN: Identifier of the attribute. |
size_t buf_size |
IN: The size of the buffer to store the name in. |
char *buf |
OUT: Buffer to store name in. |
buf_size, if successful.
Otherwise returns a negative value.
SUBROUTINE h5aget_name_f(attr_id, size, buf, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: attr_id ! Attribute identifier
INTEGER(SIZE_T), INTENT(IN) :: size ! Buffer size
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(INOUT) :: buf
! Buffer to hold attribute name
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! name length is successful,
! -1 if fail
END SUBROUTINE h5aget_name_f
H5Aget_name_by_idx(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *obj_name,
H5_index_t idx_type,
H5_iter_order_t order,
hsize_t n,
char *name,
size_t size,
hid_t lapl_id
)
H5Aget_name_by_idx retrieves
the name of an attribute that is attached to an object,
which is specified by its location and name,
loc_id and obj_name, respectively.
The attribute is located by its index position,
the size of the name is specified in size,
and the attribute name is returned in name.
If loc_id fully specifies the object to which the
attribute is attached, obj_name should be
'.' (a dot).
The attribute is located by means of an index type,
an index traversal order, and a position in the index,
idx_type, order and n,
respectively.
These parameters and their valid values are discussed in the
description of H5Aiterate2.
If the attribute name’s size is unknown,
the values 0 and NULL can be passed in
for the parameters size and name.
The function’s return value will provide
the correct value for size.
The link access property list, lapl_id,
may provide information regarding the properties of links
required to access the object, obj_name.
See “Link Access Properties” in the
H5P APIs.
hid_t loc_id
|
IN: Location of object to which attribute is attached |
const char *obj_name
|
IN: Name of object to which attribute is attached, relative to location |
H5_index_t idx_type
|
IN: Type of index |
H5_iter_order_t order
|
IN: Index traversal order |
hsize_t n
|
IN: Attribute’s position in index |
char *name
|
OUT: Attribute name |
size_t size
|
IN: Size, in bytes, of attribute name |
hid_t lapl_id
|
IN: Link access property list |
SUBROUTINE h5aget_name_by_idx_f(loc_id, obj_name, idx_type, order, &
n, name, size, lapl_id, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: loc_id ! Identifer for object to which
! attribute is attached
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: obj_name ! Name of object, relative to
! location,from which attribute is to
! be removed
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: idx_type
! Type of index; Possible values are:
! H5_INDEX_UNKNOWN_F - Unknown index type
! H5_INDEX_NAME_F - Index on names
! H5_INDEX_CRT_ORDER_F - Index on creation order
! H5_INDEX_N_F - Number indices defined
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: order ! Order in which to iterate over index:
! H5_ITER_UNKNOWN_F - Unknown order
! H5_ITER_INC_F - Increasing order
! H5_ITER_DEC_F - Decreasing order
! H5_ITER_NATIVE_F - No particular order,
! whatever is fastest
! H5_ITER_N_F - Number of iteration orders
INTEGER(HSIZE_T), INTENT(IN) :: n
! Attribute’s position in index
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(OUT) :: name
! Attribute name
INTEGER(SIZE_T), INTENT(INOUT) :: size
! Buffer size
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: lapl_id
! Link access property list
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr
! Error code:
! Returns attribute name size,
! -1 if fail
END SUBROUTINE h5aget_name_by_idx_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aget_num_attrs(
hid_t loc_id
)
H5Oget_info,
H5Oget_info_by_name, and
H5Oget_info_by_idx.
H5Aget_num_attrs returns the number of attributes
attached to the object specified by its identifier,
loc_id.
The object can be a group, dataset, or named datatype.
hid_t loc_id |
IN: Identifier of a group, dataset, or named datatype. |
SUBROUTINE h5aget_num_attrs_f(obj_id, attr_num, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: obj_id ! Object identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: attr_num ! Number of attributes of the object
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE h5aget_num_attrs_f
H5Aget_space(hid_t attr_id)
H5Aget_space retrieves a copy of the dataspace
for an attribute. The dataspace identifier returned from
this function must be released with H5Sclose
or resource leaks will develop.
hid_t attr_id |
IN: Identifier of an attribute. |
SUBROUTINE h5aget_space_f(attr_id, space_id, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: attr_id ! Attribute identifier
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(OUT) :: space_id ! Attribute dataspace identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE h5aget_space_f
H5Aget_storage_size(hid_t
attr_id)
H5Aget_storage_size returns the amount of storage
that is required for the specified attribute, attr_id.
hid_t attr_id |
IN: Identifier of the attribute to query. |
SUBROUTINE h5aget_storage_size_f(attr_id, size, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: attr_id ! Attribute identifier
INTEGER(HSIZE_T), INTENT(OUT) :: size ! Attribute storage requirement
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE h5aget_storage_size_f
H5Aget_type(hid_t attr_id)H5Aget_type retrieves a copy of the datatype
for an attribute.
The datatype is reopened if it is a named type before returning it to the application. The datatypes returned by this function are always read-only. If an error occurs when atomizing the return datatype, then the datatype is closed.
The datatype identifier returned from this function must be
released with H5Tclose or resource leaks will develop.
hid_t attr_id |
IN: Identifier of an attribute. |
SUBROUTINE h5aget_type_f(attr_id, type_id, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: attr_id ! Attribute identifier
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(OUT) :: type_id ! Attribute datatype identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE h5aget_type_f
H5Aiterate is a macro that is mapped to either
H5Aiterate1 or
H5Aiterate2,
depending on the needs of the application.
Such macros are provided to facilitate application compatibility. For example:
H5Aiterate macro
will be mapped to H5Aiterate1 and
will use the H5Aiterate1 syntax
(first signature above)
if an application is coded for HDF5 Release 1.6.x.
H5Aiterate macro
mapped to H5Aiterate2 and
will use the H5Aiterate2 syntax
(second signature above)
if an application is coded for HDF5 Release 1.8.x.
Macro use and mappings are fully described in “API Compatibility Macros in HDF5”; we urge you to read that document closely.
When both the HDF5 Library and the application are built and
installed with no specific compatibility flags,
H5Aiterate is mapped to the most recent version of
the function, currently
H5Aiterate2.
If the library and/or application is compiled for Release 1.6
emulation, H5Aiterate will be mapped to
H5Aiterate1.
Function-specific flags are available to override these settings
on a function-by-function basis when the application is compiled.
Specific compile-time compatibility flags and the resulting mappings are as follows:
| Compatibility setting | H5Aiterate mapping |
|---|---|
Global settings |
|
| No compatibility flag | H5Aiterate2 |
| Enable deprecated symbols | H5Aiterate2 |
| Disable deprecated symbols | H5Aiterate2 |
Emulate Release 1.6 interface |
H5Aiterate1 |
Function-level macros |
|
H5Aiterate_vers = 2 |
H5Aiterate2 |
H5Aiterate_vers = 1 |
H5Aiterate1 |
H5Aiterate interface
and the only interface available prior to HDF5 Release 1.8.0.
This signature and the corresponding function are now deprecated
but will remain directly callable as
H5Aiterate1.
Signature [2] above was introduced with HDF5 Release 1.8.0
and is the recommended and default interface.
It is directly callable as
H5Aiterate2.
See “API Compatibility Macros in HDF5” for circumstances under which either of these functions might not be available in an installed instance of the HDF5 Library.
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 |
The function H5Aiterate renamed to
H5Aiterate1 and deprecated in this release.
The macro H5Aiterate
and the functions H5Aiterate2
and H5Aiterate_by_name
introduced in this release. |
H5Aiterate1(
hid_t loc_id,
unsigned * idx,
H5A_operator1_t op,
void *op_data
)
H5Aiterate2.
H5Aiterate1 iterates over the attributes of
the object specified by its identifier, loc_id.
The object can be a group, dataset, or named datatype.
For each attribute of the object, the op_data
and some additional information specified below are passed
to the operator function op.
The iteration begins with the attribute specified by its
index, idx; the index for the next attribute
to be processed by the operator, op, is
returned in idx.
If idx is the null pointer, then all attributes
are processed.
The prototype for H5A_operator_t is:
typedef herr_t (*H5A_operator1_t)(hid_t loc_id,
const char *attr_name,
void *operator_data);
The operation receives the identifier for the group, dataset
or named datatype being iterated over, loc_id, the
name of the current attribute about the object, attr_name,
and the pointer to the operator data passed in to H5Aiterate1,
op_data. The return values from an operator are:
hid_t loc_id |
IN: Identifier of a group, dataset or named datatype. |
unsigned * idx |
IN/OUT: Starting (IN) and ending (OUT) attribute index. |
H5A_operator1_t op |
IN: User's function to pass each attribute to |
void *op_data |
IN/OUT: User's data to pass through to iterator operator function |
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 |
The function H5Aiterate renamed to
H5Aiterate1 and deprecated in this release. |
H5Aiterate2(
hid_t obj_id,
H5_index_t idx_type,
H5_iter_order_t order,
hsize_t *n,
H5A_operator2_t op,
void *op_data,
)
H5Aiterate2 iterates over the attributes attached to
a dataset, named datatype, or group, as specified by obj_id.
For each attribute, user-provided data, op_data,
with additional information as defined below, is passed to
a user-defined function, op, which operates on
that attribute.
The order of the iteration and the attributes iterated over are
specified by three parameters:
the index type, idx_type;
the order in which the index is to be traversed, order;
and the attribute’s position in the index, n.
The type of index specified by idx_type can be
one of the following:
H5_INDEX_NAME
| An alpha-numeric index by attribute name | ||
H5_INDEX_CRT_ORDER
| An index by creation order |
The order in which the index is to be traversed, as specified by
order, can be one of the following:
H5_ITER_INC
| Iteration is from beginning to end, i.e., a top-down iteration incrementing the index position at each step. | ||
H5_ITER_DEC
| Iteration starts at the end of the index, i.e., a bottom-up iteration decrementing the index position at each step. | ||
H5_ITER_NATIVE
| HDF5 iterates in the fastest-available order. No information is provided as to the order, but HDF5 ensures that each element in the index will be visited if the iteration completes successfully. |
The next attribute to be operated on is specified by n,
a position in the index.
For example, if idx_type, order, and
n are set to H5_INDEX_NAME,
H5_ITER_INC, and 5, respectively,
the attribute in question is the fifth attribute from the beginning
of the alpha-numeric index of attribute names.
If order were set to H5_ITER_DEC,
it would be the fifth attribute from the end of the index.
The parameter n is passed in on an H5Aiterate2
call with one value and may be returned with another value.
The value passed in identifies the parameter to be operated on first;
the value returned identifies the parameter to be operated on in the
next step of the iteration.
The H5A_operator2_t prototype for
the op parameter is as follows:
H5A_operator2_t)(
hid_t location_id/*in*/,
const char *attr_name/*in*/,
const H5A_info_t *ainfo/*in*/,
void *op_data/*in,out*/)
The operation receives the location identifier for the group or
dataset being iterated over, location_id;
the name of the current object attribute, attr_name;
the attribute’s info struct, ainfo;
and a pointer to the operator data passed into
H5Aiterate2, op_data.
Valid return values from an operator and the resulting
H5Aiterate2 and op behavior are as follows:
n.
n.
hid_t obj_id
|
IN: Identifier for object to which attributes are attached; may be group, dataset, or named datatype. |
H5_index_t idx_type
|
IN: Type of index |
H5_iter_order_t order
|
IN: Order in which to iterate over index |
hsize_t *n
|
IN/OUT: Initial and returned offset within index |
H5A_operator2_t op
|
IN: User-defined function to pass each attribute to |
void *op_data
|
IN/OUT: User data to pass through to and to be returned by iterator operator function |
Further note that this function returns the return value of the last operator if it was non-zero, which can be a negative value, zero if all attributes were processed, or a positive value indicating short-circuit success (see above).
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aiterate_by_name(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *obj_name,
H5_index_t idx_type,
H5_iter_order_t order,
hsize_t *n,
H5A_operator2_t op,
void *op_data,
hid_t lapd_id
)
H5Aiterate_by_name iterates over the attributes
attached to the dataset or group specified with loc_id and
obj_name.
For each attribute, user-provided data, op_data,
with additional information as defined below, is passed to
a user-defined function, op, which operates on
that attribute.
If loc_id fully specifies the object to which these
attributes are attached, obj_name should be
'.' (a dot).
The order of the iteration and the attributes iterated over are
specified by three parameters:
the index type, idx_type;
the order in which the index is to be traversed, order;
and the attribute’s position in the index, n.
The type of index specified by idx_type can be
one of the following:
H5_INDEX_NAME
| An alpha-numeric index by attribute name | ||
H5_INDEX_CRT_ORDER
| An index by creation order |
The order in which the index is to be traversed, as specified by
order, can be one of the following:
H5_ITER_INC
| Iteration is from beginning to end, i.e., a top-down iteration incrementing the index position at each step. | ||
H5_ITER_DEC
| Iteration starts at the end of the index, i.e., a bottom-up iteration decrementing the index position at each step. | ||
H5_ITER_NATIVE
| HDF5 iterates in the fastest-available order. No information is provided as to the order, but HDF5 ensures that each element in the index will be visited if the iteration completes successfully. |
The next attribute to be operated on is specified by n,
a position in the index.
For example, if idx_type, order, and
n are set to H5_INDEX_NAME,
H5_ITER_INC, and 5, respectively,
the attribute in question is the fifth attribute from the beginning
of the alpha-numeric index of attribute names.
If order were set to H5_ITER_DEC,
it would be the fifth attribute from the end of the index.
The parameter n is passed in on an
H5Aiterate_by_name call with one value and may be
returned with another value.
The value passed in identifies the parameter to be operated on first;
the value returned identifies the parameter to be operated on in the
next step of the iteration.
The H5A_operator2_t prototype for
the op parameter is as follows:
H5A_operator2_t)(
hid_t location_id/*in*/,
const char *attr_name/*in*/,
const H5A_info_t *ainfo/*in*/,
void *op_data/*in,out*/)
The operation receives the location identifier for the group or
dataset being iterated over, location_id;
the name of the current object attribute, attr_name;
the attribute’s info struct, ainfo;
and a pointer to the operator data passed into
H5Aiterate_by_name, op_data.
Valid return values from an operator and the resulting
H5Aiterate_by_name and op behavior are
as follows:
n.
n.
The link access property list, lapl_id,
may provide information regarding the properties of links
required to access the object, obj_name.
See “Link Access Properties” in the
H5P APIs.
hid_t loc_id
|
IN: Location or object identifier; may be dataset or group |
const char *obj_name
|
IN: Name of object, relative to location |
H5_index_t idx_type
|
IN: Type of index |
H5_iter_order_t order
|
IN: Order in which to iterate over index |
hsize_t *n
|
IN/OUT: Initial and returned offset within index |
H5A_operator2_t op
|
IN: User-defined function to pass each attribute to |
void *op_data
|
IN/OUT: User data to pass through to and to be returned by iterator operator function |
hid_t lapd_id
|
IN: Link access property list |
Further note that this function returns the return value of the last operator if it was non-zero, which can be a negative value, zero if all attributes were processed, or a positive value indicating short-circuit success (see above).
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aopen(
hid_t obj_id,
const char *attr_name,
hid_t aapl_id
)
H5Aopen
opens an existing attribute, attr_name,
that is attached to an object specified an object identifier,
object_id.
The attribute access property list, aapl_id,
is currently unused and should currently be H5P_DEFAULT.
This function,
H5Aopen_by_idx, or
H5Aopen_by_name
must be called before an attribute can be accessed for any
further purpose, including reading, writing, or any modification.
The attribute identifier returned by this function must be released
with H5Aclose
or resource leaks will develop.
hid_t obj_id
|
IN: Identifer for object to which attribute is attached |
const char *attr_name
|
IN: Name of attribute to open |
hid_t aapl_id
|
IN: Attribute access property list |
SUBROUTINE h5aopen_f(obj_id, attr_name, attr_id, hdferr, aapl_id)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: obj_id ! Object identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: attr_name ! Attribute name
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(OUT) :: attr_id ! Attribute identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: aapl_id
! Attribute access property list
END SUBROUTINE h5aopen_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aopen_by_idx(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *obj_name,
H5_index_t idx_type,
H5_iter_order_t order,
hsize_t n,
hid_t aapl_id,
hid_t lapl_id
)
H5Aopen_by_idx opens an existing attribute
that is attached to an object specified by location and name,
loc_id and obj_name, respectively.
If loc_id fully specifies the object to which the
attribute is attached, obj_name should be
'.' (a dot).
The attribute is identified by an index type, an index traversal order,
and a position in the index, idx_type,
order and n, respectively.
These parameters and their valid values are discussed in the
description of H5Aiterate2.
The attribute access property list, aapl_id,
is currently unused and should currently be H5P_DEFAULT.
The link access property list, lapl_id,
may provide information regarding the properties of links
required to access the object, obj_name.
See “Link Access Properties” in the
H5P APIs.
This function,
H5Aopen, or
H5Aopen_by_name
must be called before an attribute can be accessed for any
further purpose, including reading, writing, or any modification.
The attribute identifier returned by this function must be released
with H5Aclose
or resource leaks will develop.
hid_t loc_id
|
IN: Location of object to which attribute is attached |
const char *obj_name
|
IN: Name of object to which attribute is attached, relative to location |
H5_index_t idx_type
|
IN: Type of index |
H5_iter_order_t order
|
IN: Index traversal order |
hsize_t n
|
IN: Attribute’s position in index |
hid_t aapl_id
|
IN: Attribute access property list |
hid_t lapl_id
|
IN: Link access property list |
SUBROUTINE h5aopen_by_idx_f(loc_id, obj_name, idx_type, order, n, attr_id, &
hdferr, aapl_id, lapl_id)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: loc_id
! Object identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: obj_name
! Name of object to which attribute is attached
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: idx_type
! Type of index; Possible values are:
! H5_INDEX_UNKNOWN_F - Unknown index type
! H5_INDEX_NAME_F - Index on names
! H5_INDEX_CRT_ORDER_F - Index on creation order
! H5_INDEX_N_F - Number of indices defined
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: order
! Order in which to iterate over index:
! H5_ITER_UNKNOWN_F - Unknown order
! H5_ITER_INC_F - Increasing order
! H5_ITER_DEC_F - Decreasing order
! H5_ITER_NATIVE_F - No particular order,
! whatever is fastest
INTEGER(HSIZE_T), INTENT(IN) :: n
! Attribute’s position in index
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(OUT) :: attr_id
! Attribute identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr
! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: aapl_id
! Attribute access property list
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: lapl_id
! Link access property list
END SUBROUTINE h5aopen_by_idx_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aopen_by_name(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *obj_name,
const char *attr_name,
hid_t aapl_id,
hid_t lapl_id
)
H5Aopen_by_name
opens an existing attribute, attr_name,
that is attached to an object specified by location and name,
loc_id and obj_name, respectively.
loc_id specifies a location from which the
target object can be located and obj_name is an
object name relative to loc_id.
If loc_id fully specifies the object to which the
attribute is attached, obj_name should be
'.' (a dot).
The attribute access property list, aapl_id,
is currently unused and should currently be H5P_DEFAULT.
The link access property list, lapl_id,
may provide information regarding the properties of links
required to access the object, obj_name.
See “Link Access Properties” in the
H5P APIs.
This function,
H5Aopen, or
H5Aopen_by_idx
must be called before an attribute can be accessed for any
further purpose, including reading, writing, or any modification.
The attribute identifier returned by this function must be released
with H5Aclose
or resource leaks will develop.
hid_t loc_id
|
IN: Location from which to find object to which attribute is attached |
const char *obj_name
|
IN: Name of object to which attribute is attached,
relative to loc_id
|
const char *attr_name
|
IN: Name of attribute to open |
hid_t aapl_id
|
IN: Attribute access property list
(Currently unused; should be passed in as H5P_DEFAULT.)
|
hid_t lapl_id
|
IN: Link access property list |
SUBROUTINE h5aopen_by_name_f(loc_id, obj_name, attr_name, attr_id, hdferr, &
aapl_id, lapl_id)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: loc_id
! Location identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: obj_name
! Object name either relative to loc_id,
! absolute from file’s root group, or '.'
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: attr_name
! Attribute name
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(OUT) :: attr_id
! Attribute identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: aapl_id
! Attribute access property list
! (Currently unused; set to H5P_DEFAULT_F)
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: lapl_id
! Link access property list identifier
END SUBROUTINE
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Aopen_idx(
hid_t loc_id,
unsigned int idx
)
H5Aopen_by_idx.
H5Aopen_idx opens an attribute which is attached
to the object specified with loc_id.
The location object may be either a group, dataset, or
named datatype, all of which may have any sort of attribute.
The attribute specified by the index, idx,
indicates the attribute to access.
The value of idx is a 0-based, non-negative integer.
The attribute identifier returned from this function must be
released with H5Aclose or resource leaks will develop.
hid_t loc_id |
IN: Identifier of the group, dataset, or named datatype attribute to be attached to. |
unsigned int idx |
IN: Index of the attribute to open. |
SUBROUTINE h5aopen_idx_f(obj_id, index, attr_id, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: obj_id ! Object identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(IN) :: index ! Attribute index
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(OUT) :: attr_id ! Attribute identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE h5aopen_idx_f
H5Aopen_name(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *name
)
H5Aopen_by_name.
H5Aopen_name opens an attribute specified by
its name, name, which is attached to the
object specified with loc_id.
The location object may be either a group, dataset, or
named datatype, which may have any sort of attribute.
The attribute identifier returned from this function must
be released with H5Aclose or resource leaks
will develop.
hid_t loc_id |
IN: Identifier of a group, dataset, or named datatype that attribute is attached to. |
const char *name |
IN: Attribute name. |
SUBROUTINE h5aopen_name_f(obj_id, name, attr_id, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: obj_id ! Object identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: name ! Attribute name
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(OUT) :: attr_id ! Attribute identifier
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE h5aopen_name_f
H5Aread(hid_t attr_id,
hid_t mem_type_id,
void *buf
)
H5Aread reads an attribute, specified with
attr_id. The attribute's memory datatype
is specified with mem_type_id. The entire
attribute is read into buf from the file.
Datatype conversion takes place at the time of a read or write and is automatic. See the “Data Transfer: Datatype Conversion and Selection” section in the “HDF5 Datatypes” chapter of the HDF5 User’s Guide for a discussion of data conversion.
hid_t attr_id |
IN: Identifier of an attribute to read. |
hid_t mem_type_id |
IN: Identifier of the attribute datatype (in memory). |
void *buf |
OUT: Buffer for data to be read. |
SUBROUTINE h5aread_f(attr_id, memtype_id, buf, dims, hdferr)
INTEGER(HID_T) , INTENT(IN) :: attr_id
INTEGER(HID_T) , INTENT(IN) :: memtype_id
TYPE , INTENT(INOUT) :: buf
INTEGER(HSIZE_T), INTENT(IN), DIMENSION(*) :: dims
INTEGER , INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr
Inputs:
attr_id - Attribute identifier
memtype_id - Attribute datatype identifier (in memory)
dims - Array to hold corresponding dimension sizes of data buffer buf;
dim(k) has value of the k-th dimension of buffer buf;
values are ignored if buf is a scalar
Outputs:
buf - Data buffer; may be a scalar or an array hdferr - Returns 0 if successful and -1 if fails
SUBROUTINE h5aread_f(attr_id, memtype_id, buf, hdferr)
INTEGER(HID_T) , INTENT(IN) :: attr_id
INTEGER(HID_T) , INTENT(IN) :: memtype_id
TYPE(C_PTR) , INTENT(INOUT) :: buf
INTEGER , INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr
Inputs:
attr_id - Attribute identifier memtype_id - Attribute datatype identifier (in memory)
Outputs:
buf - Data buffer; may be a scalar or an array hdferr - Returns 0 if successful and -1 if fails
| Release | Fortran |
| 1.8.8 | Fortran updated to Fortran2003. |
| 1.4.2 |
The dims parameter was added in this release. |
H5Arename(
hid_t loc_id,
char *old_attr_name,
char *new_attr_name
)
H5Arename changes the name of the attribute
located at loc_id.
The old name, old_attr_name, is changed
to the new name, new_attr_name.
hid_t loc_id |
IN: Location of the attribute. |
char *old_attr_name |
IN: Name of the attribute to be changed. |
char *new_attr_name |
IN: New name for the attribute. |
SUBROUTINE h5arename_f(loc_id, old_attr_name, new_attr_name, hdferr)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: loc_id ! Object identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: old_attr_name ! Prior attribute name
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: new_attr_name ! New attribute name
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success, -1 on failure
END SUBROUTINE h5arename_f
H5Arename_by_name(
hid_t loc_id,
const char *obj_name,
const char *old_attr_name,
const char *new_attr_name,
hid_t lapl_id
)
H5Arename_by_name changes the name of attribute that is
attached to the object specified by loc_id and
obj_name. The attribute named old_attr_name
is renamed new_attr_name.
The link access property list, lapl_id,
may provide information regarding the properties of links
required to access the object, obj_name.
See “Link Access Properties” in the
H5P APIs.
hid_t loc_id
|
IN: Location or object identifier; may be dataset or group |
const char *obj_name
|
IN: Name of object, relative to location, whose attribute is to be renamed |
const char *old_attr_name
|
IN: Prior attribute name |
const char *new_attr_name
|
IN: New attribute name |
hid_t lapl_id
|
IN: Link access property list identifier |
SUBROUTINE h5arename_by_name_f(loc_id, obj_name, old_attr_name, new_attr_name, &
hdferr, lapl_id)
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER(HID_T), INTENT(IN) :: loc_id ! Object identifier
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: obj_name
! Name of object, relative to location,
! whose attribute is to be renamed
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: old_attr_name
! Prior attribute name
CHARACTER(LEN=*), INTENT(IN) :: new_attr_name
! New attribute name
INTEGER, INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr ! Error code:
! 0 on success and -1 on failure
INTEGER(HID_T), OPTIONAL, INTENT(IN) :: lapl_id
! Link access property list identifier
END SUBROUTINE h5arename_by_name_f
| Release | C |
| 1.8.0 | Function introduced in this release. |
H5Awrite(hid_t attr_id,
hid_t mem_type_id,
const void *buf
)
H5Awrite writes an attribute, specified with
attr_id. The attribute's memory datatype
is specified with mem_type_id. The entire
attribute is written from buf to the file.
If mem_type_id is either a fixed-length or
variable-length string, it is important to set the string length
when defining the datatype.
String datatypes are derived from H5T_C_S1
(or H5T_FORTRAN_S1 for Fortran codes),
which defaults to 1 character in size.
See H5Tset_size
and “Creating
variable-length string datatypes.”
Datatype conversion takes place at the time of a read or write and is automatic. See the “Data Transfer: Datatype Conversion and Selection” section in the “HDF5 Datatypes” chapter of the HDF5 User’s Guide for a discussion of data conversion.
hid_t attr_id |
IN: Identifier of an attribute to write. |
hid_t mem_type_id |
IN: Identifier of the attribute datatype (in memory). |
const void *buf |
IN: Data to be written. |
SUBROUTINE h5awrite_f(attr_id, memtype_id, buf, dims, hdferr)
INTEGER(HID_T) , INTENT(IN) :: attr_id
INTEGER(HID_T) , INTENT(IN) :: memtype_id
TYPE , INTENT(IN) :: buf
INTEGER(HSIZE_T), INTENT(IN), DIMENSION(*) :: dims
INTEGER , INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr
Inputs:
attr_id - Attribute identifier
memtype_id - Attribute datatype identifier (in memory)
dims - Array to hold corresponding dimension sizes of data buffer buf;
dim(k) has value of the k-th dimension of buffer buf;
values are ignored if buf is a scalar
buf - Data buffer; may be a scalar or an array
Outputs:
hdferr - Returns 0 if successful and -1 if fails
SUBROUTINE h5awrite_f(attr_id, memtype_id, buf, hdferr)
INTEGER(HID_T) , INTENT(IN) :: attr_id
INTEGER(HID_T) , INTENT(IN) :: memtype_id
TYPE(C_PTR) , INTENT(IN) :: buf
INTEGER , INTENT(OUT) :: hdferr
Inputs:
attr_id - Attribute identifier memtype_id - Attribute datatype identifier (in memory) buf - Data buffer; may be a scalar or an array
Outputs:
hdferr - Returns 0 if successful and -1 if fails
H5Tset_size
| Release | Change |
| 1.8.8 | Fortran updated to Fortran2003. |
| 1.4.2 |
Fortran dims parameter added in this release. |